Signs It Could Be More Than a Cold

Symptoms Come On Fast
When you have a cold, symptoms like a stuffy nose or sneezing start slowly and gradually get worse. Flu symptoms typically hit your body all of a sudden -- and they'll probably feel a lot stronger.

Chills
This is when you shiver because your body temperature changes. Chills aren’t typical signs of a cold -- they’re an early sign of infection and high fever. They're more common with flu, pneumonia, or COVID-19.
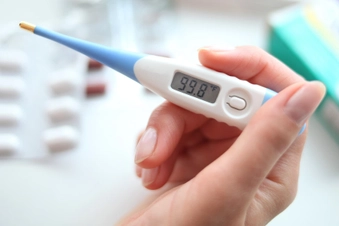
Increase in Temperature
This is a sign that your body is trying to fight an illness or infection, but it's rarely caused by a cold. Flu, bronchitis, pneumonia, and COVID-19 are more common causes of fevers. You are considered to have a fever when your temperature reaches 100.5 F.

Body Aches
You may have some slight body aches with a cold, but stronger ones are usually a sign that you have the flu or COVID-19. This is because short-term achy muscles often happen along with a fever.
Wheezing
This is when your breathing sounds like a whistle. If you wheeze, it’s a sign of a more serious infection like pneumonia or bronchitis, especially if it happens when you lie down. Wheezing also can be a sign of anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction to something you ate or an insect bite.

Cough With Mucus
You may have a mild, pesky cough from a cold, but if you cough up mucus -- slimy stuff from deep down in your chest -- it can be a sign of bronchitis or pneumonia, especially if there's blood in it. COVID-19 usually causes you to have a dry cough, but it can sometimes also make you cough up mucus. It's possible to cough up blood with COVID-19, but this is rare.

Fatigue
Feeling like you have no energy or appetite is a typical symptom of the flu -- it’s less often caused by a cold. It can also be a sign of COVID-19, pneumonia or a sinus infection, which is common but more serious than a cold.
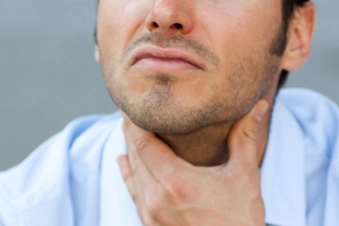
Sore Throat
A mild one is a typical symptom of a cold and sometimes the flu. It should clear up once your cold or flu does. But a very painful sore throat that comes on quickly can be a sign of strep throat. That’s a bacterial infection that should be treated with antibiotics. A sore throat is also common with COVID-19.
Headache
Many things can cause this, but a cold isn't usually one of them. It's a common flu and COVID-19 symptom and can be a sign of a sinus infection. But painful sinuses, the spaces above and around your nose, can also be caused by hay fever or rhinitis.

Chest Tightness or Pain
This is a telltale symptom of a more serious respiratory infection, like bronchitis. That can also make your chest feel tight, and you may have a hard time taking a deep breath. Sharp chest pain that feels worse when you cough can be a sign of pneumonia, and chest tightness is also a common symptom of asthma. Get medical help right away for any chest pain or pressure. It can also be the sign of life threatening conditions such as a heart attack or a blood clot in the lung.
Shortness of Breath
Colds can cause a very stuffy nose, which make breathing a little harder, but real shortness of breath is a sign of something more serious. It's a common symptom of asthma or a flare-up of COPD, and it also can be from a serious infection, like bronchitis, pneumonia, or COVID-19.

Ear, Face, or Eye Pressure
If you feel pressure in your ears, it may mean you have a sinus infection. That also causes pain and pressure around your eyes, cheeks, or forehead that gets worse when you bend over. And if you feel fullness in one ear, it may be a symptom of an ear infection.

Symptoms That Don't Go Away
Flu symptoms may be bad, but they usually get better within a few days. A cold can last up to 10 days. But pneumonia symptoms can stick around up to a month or longer. And those from COVID-19 or bronchitis can last several months in some cases. Call your doctor right away for any new or worsening symptom so that the right diagnosis can be made and you can get the right treatment.
Show Sources
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
1) kieferpix / Getty Images
2) S-Attila / Images
3) Foremniakowski / Getty Images
4) AHPhotoswpg / Getty Images
5) yacobchuk / Getty Images
6) bert_phantana / Thinkstock
7) eldinhoid / Getty Images
8) AdamGregor / Getty Images
9) Sebastian Kaulitzki / Thinkstock
10) AntonioGuillem / Getty Images
11) wildpixel / Getty Images
12) seb_ra / Getty Images
13) baloon111 / Getty Images
SOURCES:
CDC: “Cold Versus Flu,” “Strep Throat: All You Need to Know,” "Symptoms of COVID-19."
MedlinePlus.gov: "Fever.”
Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition: “Chapter 211: Fevers, Chills, and Night Sweats.”
Nicklaus Children’s Hospital: “Chills.”
American Lung Association: “Pneumonia,” “Shortness of Breath: Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors.”
Asthma UK: “Symptoms of Asthma.”
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: “Bronchitis.”
Mayo Clinic: “Fever,” “Wheezing,” “Food Allergy,” “Acute Sinusitis,” “Fatigue Causes.”
Harvard Medical School: “Influenza: how to prevent and treat a serious infection,” “How long does the flu last?”
FamilyDoctor.org: “When a Chest Cold Is Something More.”
American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology: “Headaches Connected to Allergies and Sinus Problems,” “Rhinitis (Hay Fever),” “Sinus Infection.”
Teens Health From Nemours: “Coping With Colds (For Teens).”
Cleveland Clinic: “Pediatric Ear Infections.”
NHS Inform: "Long COVID: Cough."
BMC Pulmonary Medicine: “Haemoptysis as the first presentation of COVID-19: a case report.”

